Project B02: Nano Lett. 2018
Efficient Emission Enhancement of Single CdSe/CdS/PMMA Quantum Dots through Controlled Near-Field Coupling to Plasmonic Bullseye Resonators
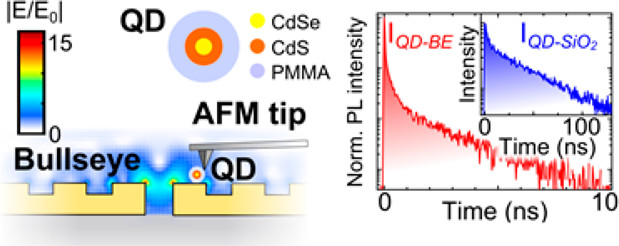
A strong increase of spontaneous radiative emission from colloidally synthesized CdSe/CdS/PMMA hybrid particles is achieved when manipulated into plasmonic bullseye resonators with the tip of an atomic force microscope (AFM). This type of antenna provides a broadband resonance, which may be precisely matched to the exciton ground state energy in the inorganic cores. Statistically analyzing the spectral photoluminescence (PL) of a large number of individual coupled and uncoupled CdSe/CdS/PMMA quantum dots, we find an order of magnitude of intensity enhancement due to the Purcell effect. Time-resolved PL shows a commensurate increase of the spontaneous emission rate with radiative lifetimes below 230 ps for the bright exciton transition. The combination of AFM and PL imaging allows for sub-200 nm localization of the particle position inside the plasmonic antenna. This capability unveils a different coupling behavior of dark excitonic states: even stronger PL enhancement occurs at positions with maximum spatial gradient of the nearfield, effectively adding a dipolar component to original quadrupole transitions. The broadband maximization of light-matter interaction provided by our nanoengineered compound systems enables an attractive class of future experiments in ultrafast quantum optics.
F. Werschler, B. Lindner, C. Hinz, F. Conradt, P. Gumbsheimer, Y. Behovits, C. Negele, T. de Roo, O. Tzang, S. Mecking, A. Leitenstorfer, D. V. Seletskiy
Nano Lett. 18, 5396 (2018)
DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b01533
